peach tree borer life cycle
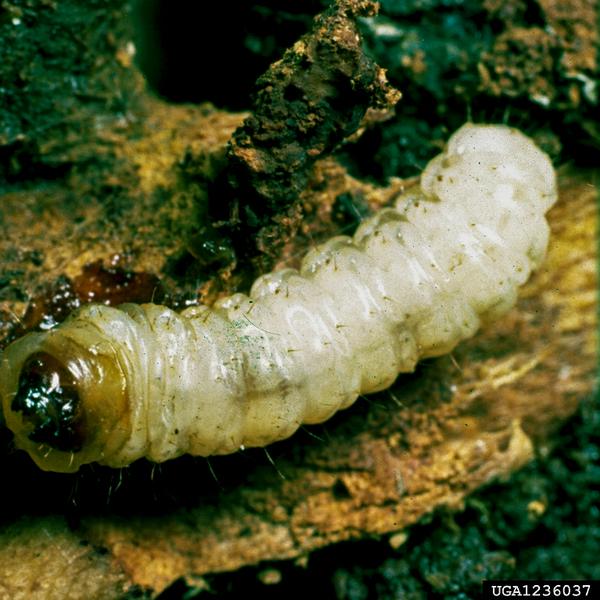
Winter is spent as a larva under the bark in the cambium layer. Larvae of the peachtree borer found mainly in coastal areas and in the northern San Joaquin Valley are white with brown heads.

Peach Tree Borers How To Control Peach Tree Borers
Seasonal development and life cyclePeachtree borer.

. As temperatures rise above 50F in the spring the larva resumes feeding on the tissues under the bark. The adult peachtree borer may be found from May to September. Lesser peachtree borers Synanthedon pictipes.
Description and Life Cycle. Lesser peachtree borer S. Only the immature larva stage Figure 3 produces the damage to trees.
At maturity in May and June the larva pupates. The peachtree borer overwinters as a partly grown larva in its burrow beneath the bark of the tree. LPTB are clearwing moths native to North America and capable of causing economically significant damage to peach cherry plum nectarine and apricot trees.
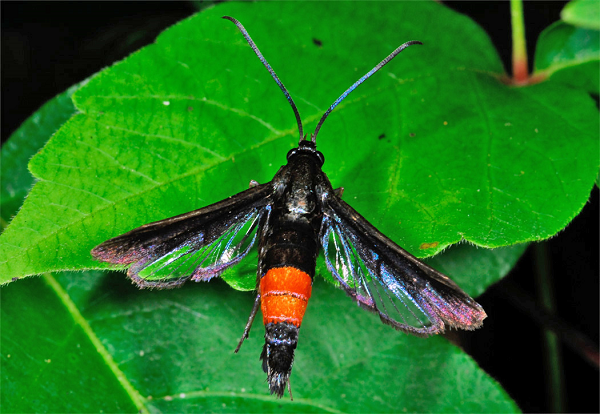
An amber-colored gum gummosis is. Pictipes adults have clear wings and metallic blue bodies with yellow markings. As temperatures warm up they resume boring and usually complete their feeding in May.
To survive they must get under dead bark near live bark where they have protection for feeding. Adult LPTB strongly resemble small wasps having dark blue bodies with yellow bands on the second and fourth abdominal segments and. The grub-like larvae chew underneath the bark at.
Life cycles of peachtree borers and lesser peachtree borers. Female moths lay their eggs during the summer on bark at the base of tree trunks. The lesser borer completes about one and one-half cycles a year.
In the spring feeding is resumed and the larval period is completed. Purple sand cherry Prunus x cistena is highly susceptible to peachtree borer. The moths fly during the day and closely resemble paper wasps the moths do not sting.
It is reported that it takes two years to complete a life cycle in Canada and in a small percentage of populations in New York. Weve said no to GMOs. Because the egg laying period is so long overwintering larvae vary greatly in size.
Larvae feed on branches near or in trunk crotches and at old trunk wound sites found above ground level. Free Shipping 10 off lawn garden more when you join the Stay Green Garden Club. These borers are caterpillars of a dark clearwinged moth.
Upon hatching from eggs young larvae immediately tunnel into the sapwood of the tree usually through cracks and wounds in the bark. It is a pest of flowering cherry and almond. Damage Any wound on stone fruit trees may cause gum to exude.
The life cycle of the peachtree borer requires one year to complete. When mature the larva constructs a cocoon under the bark at or near soil level and pupates. Adult peachtree borers emerge in the late spring or early summer.
The 3 4 -inch-long females are bluish black with an orange band on the abdomen. Gum exuding from around the base of the trunk is evidence of peachtree borer. Life Cycle and Damage Peach tree borers overwinter as partially grown larvae in a gallery under the bark.
Much of the United States including Texas and Nebraska has one generation per year. Look for injury symptoms when pruning trees in the spring and early summer. The peach tree borer completes one life cycle a year.
Adult moths of the lesser peachtree borer emerge from late May through September while peachtree borers emerge from midJune to early September. For decades the greater peachtree borer Synanthedon exitisoa was known simply as the peachtree borer. Usually they are close to or below ground level.
Biology and life history The borer overwinters as a larva on or under the tree bark usually below ground. Ad We are actual gardeners experts that test evaluate each product. Hatching larvae tunnel into the tree at or slightly below ground level.
Egg laying begins soon after emergence and mating and larvae tunnel into the bark to feed until the. Adults are clear-winged moths with blue-black bodies having yellow or orange bands across the abdomen. Eggs hatch in 8 to 30 days and the larvae attempt to bore into the bark.
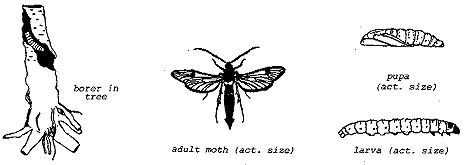
Peachtree borer life cycle showing larva 1 cocoon 2 empty pupal case 3 and cocoon with pupa emerging 43 bark of the lower trunk or in the soil near the trunk base or by a larva andor larval tunnel under the bark Fig. Adult moths emerge beginning in June. The period of time required to complete a life cycle varies considerably throughout the range of the peachtree borer.
Larvae of the peachtree borer cause damage to fruit trees. Larvae range from 125 to 35 cm in length and are white with a brown head.

Peachtree Borer Oklahoma State University

Peach Tree Borer Treatment Control Planet Natural

Peach And Nectarine Peachtree Borer Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks

Peach Tree Borer Fairfax Gardening

Lesser Peachtree Borer Damage Stock Image C025 7085 Science Photo Library
Pests Bc Tree Fruit Production Guide
Peachtree Borer Wsu Tree Fruit Washington State University
Eny 691 In489 Peachtree Borers In The Home And Commercial Peach Orchard

Peachtree Borer Oklahoma State University
Lords Environmental Peach Tree Borers

Peach And Nectarine Peachtree Borer Pacific Northwest Pest Management Handbooks

Peach Tree Borer Trap Pest Control From Gardens Alive

Peachtree Borer Nc State Extension Publications

Peachtree Borer Nc State Extension Publications

Peachtree Borer Nectarine Agriculture Pest Management Guidelines Uc Statewide Ipm Program Uc Ipm



